Data Governance in Databricks
Databricks is a unified set of tools for building, deploying, sharing, and maintaining enterprise-grade data solutions at scale. The Databricks Lakehouse Platform integrates with cloud storage and security in your cloud account, and manages and deploys cloud infrastructure on your behalf.
What is Databricks used for?
Our customers use Databricks to process, store, clean, share, analyse, model, and monetize their datasets with solutions from BI to machine learning. Use the Databricks platform to build and deploy data engineering workflows, machine learning models, analytics dashboards, and more.
The Databricks workspace provides a unified interface and tools for most data tasks, including:
- Data processing workflows scheduling and management
- Working in SQL
- Generating dashboards and visualizations
- Data ingestion
- Managing security, governance, and HA/DR
- Data discovery, annotation, and exploration
- Compute management
- Machine learning (ML) modelling and tracking
- ML model serving
- Source control with Git
In addition to the workspace UI, you can interact with Databricks programmatically with the following tools:
- REST API
- CLI
- Terraform
What is data governance?
Data governance is a comprehensive approach that comprises the principles, practices and tools to manage an organization’s data assets throughout their lifecycle. By aligning data-related requirements with business strategy, data governance provides superior data management, quality, visibility, security and compliance capabilities across the organization. Implementing an effective data governance strategy allows companies to make data easily available for data-driven decision-making while safeguarding their data from unauthorized access, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
What are the business benefits of data governance?
Data governance is essential for unlocking the value of data, which is a critical asset for organizations. By implementing a robust data governance approach, businesses can leverage their data assets, gain a competitive edge, and earn and maintain customer trust by ensuring sound data and privacy practices.
Increased operational efficiency and reduced costs
Effective data governance allows organizations to create a single source of truth for their data estate, preventing data sprawl and silos, and reducing duplication. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs and easier management of security and governance concepts across the data estate.
Improved productivity and faster decision-making
Data governance promotes data democratization by ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness. It helps data users find high-quality data quickly, promoting a better understanding of the data’s meaning and context, leading to increased productivity and faster decision-making.
Enhanced collaboration and value realization
A strong data governance program lays the foundation for enhanced data collaboration and sharing across teams, business units, and partners. This helps organizations promote knowledge sharing and build a better data culture, leading to increased innovation, better decision-making, and maximizing the value of their data.
Enhanced security and privacy
Data governance mitigates security and privacy risks by implementing controls and processes to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive data. It promotes a culture of trust and transparency with stakeholders.
Better compliance with regulations and standards
Effective data governance results in better compliance with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, FedRAMP, GDPR or CCPA. This protects the organization’s reputation, avoids potential financial and legal consequences, and increases stakeholder trust.
Key elements of data governance:
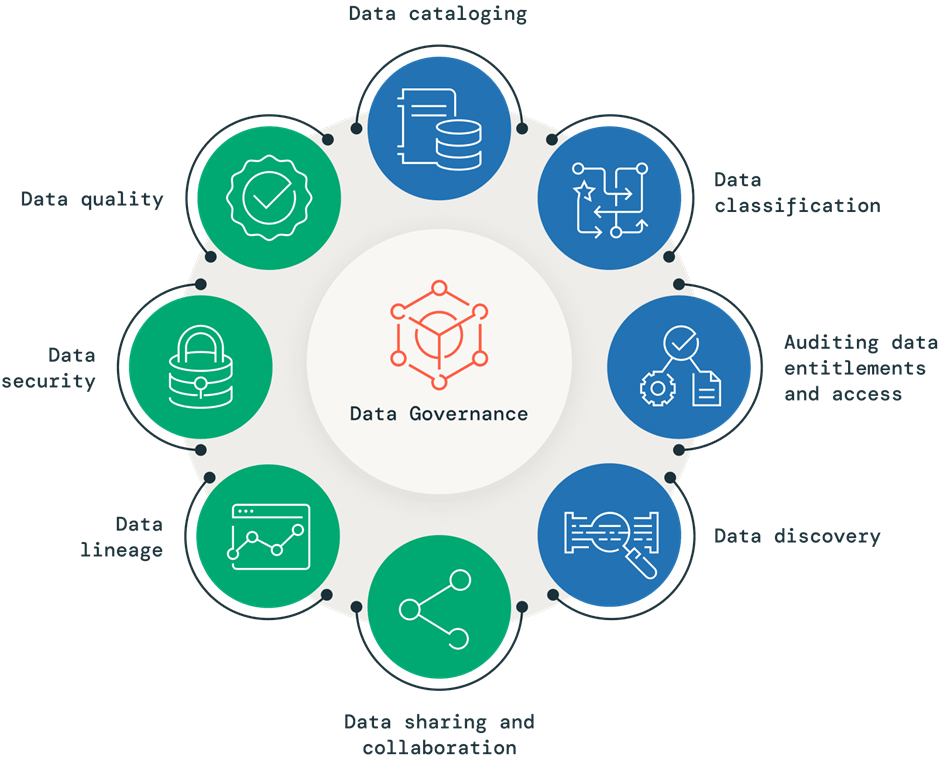

Data cataloguing
Effective data governance requires knowledge of the data that exists within an organization. This is where a data catalog comes in, as it provides a centralized metadata repository for an organization’s data assets. A data catalog allows stakeholders to quickly discover, understand and access the data they need, improving data-related activities such as discovery, governance and analytics. It acts as a searchable index of all the data available, including information about its format, structure, location and usage, providing semantic value to an otherwise unidentifiable sea of information. Incorporating a data catalog into a governance program can help organizations improve their data management, enhance collaboration, reduce redundancy and ensure proper access controls and audit information retrieval.

Data quality
In today’s data-driven world, ensuring high data quality is crucial for accurate analytics, informed decision-making and cost-effectiveness. Data quality directly impacts the reliability of data-driven decisions and is a key aspect of data governance. To maintain effective data governance, organizations must prioritize the evaluation of key data quality attributes such as accuracy, completeness, freshness and compliance with data-quality rules. Therefore, a strong focus on data quality is essential in any data governance strategy, as it helps trace data lineage, enforce data quality rules, and track changes. Don’t let poor data quality compromise your business decisions and resource allocation — prioritize data quality as a critical part of your data governance efforts for better outcomes.

Data classification
Data classification is a crucial part of data governance that involves organizing and categorizing data based on its sensitivity, value and criticality. With the exponential growth of data, businesses are increasingly concerned about protecting sensitive data, mitigating risks and ensuring data quality. Classification allows organizations to identify and classify data based on its risk level and importance, allowing them to apply appropriate security measures and policies. A robust data classification system enhances data governance, reduces risks and ensures data quality and protection at scale.

Data security
Organizations understand the significance of granting high-quality data access to their teams to drive insights and business value, while prioritizing sensitive data protection against unauthorized access. Effective data access management is crucial for data security and governance, and a good data security governance program should include access controls that define which groups or individuals can access what data. These controls can be highly specific, down to the individual record or file. As data breaches and regulations such as GDPR and CCPA pose increased risks, businesses must establish clear governance policies that define who can access sensitive data sets and how to track any misuse. Unauthorized access to private or sensitive information should not occur, and implementing effective access management strategies is essential to safeguard data and maintain customer trust.

Auditing data entitlements and access
Effective data access auditing is a critical aspect of data governance and security governance programs, particularly in regulated industries. By understanding who has access to what data and tracking recent access, organizations can proactively identify overentitled users or groups and adjust their access accordingly, minimizing the risk of data misuse. Without proper audit mechanisms in place, an organization may not be fully aware of their risk surface area, leaving them vulnerable to data breaches and regulatory noncompliance. Therefore, a well-designed audit team within a data governance or security governance organization plays a key role in ensuring data security and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. By implementing effective data access auditing strategies, organizations can maintain the trust of their customers and protect their data from unauthorized access or misuse.

Data lineage
Data lineage is a powerful tool that helps organizations ensure data quality and trustworthiness by providing a better understanding of data sources and consumption. It captures relevant metadata and events throughout the data’s lifecycle, providing an end-to-end view of how data flows across an organization’s data estate. As an essential pillar of a pragmatic data governance strategy, data lineage enables organizations to become compliant and audit-ready while reducing the operational overhead of creating audit trails manually, and providing trusted sources for audit reports. Additionally, data lineage empowers data consumers to perform better analyses, and helps data teams perform root cause analysis of any errors, significantly reducing debugging time.

Data discovery
As organizations continue to gather massive amounts of data from various sources, it’s becoming increasingly important to make this data easily discoverable for analytics, AI or ML use cases. This is critical to accelerate data democratization and unlock the true value of the data. Furthermore, with the emergence of modern data assets like dashboards, machine learning models, queries, libraries and notebooks, data discovery has become a key pillar of a robust data governance strategy. Organizations should view data discovery as a fundamental aspect of their data governance strategy. It enables data teams to easily locate data assets across the organization, collaborate on various projects, and innovate quickly and efficiently. This helps to prevent data duplication, which can be problematic as it costs money to persist them, and may lead to governance challenges at different security levels.
Data sharing and collaboration
Data sharing and collaboration are vital components in today’s business environment, with organizations exchanging data with internal teams, external partners, and customers across multiple clouds, data platforms and regions. As the demand for external data continues to grow, it is critical for organizations to securely exchange data while maintaining control and visibility over how their sensitive information is used. Data cleanrooms play a critical role in secure and controlled data collaboration, ensuring that data privacy regulations are upheld. It is essential for organizations to invest in open format, interoperable and multicloud data sharing technologies to meet their data-driven innovation needs. Moreover, data marketplaces serve as a bridge between data providers and consumers, facilitating the discovery and distribution of data sets. Therefore, it is crucial to recast data sharing as a business necessity and a crucial pillar of a robust data governance strategy.
Conclusion
Databricks is a powerful platform that offers a comprehensive set of tools for organizations to process, store, clean, share, analyze, model, and monetize their datasets at scale. With its unified interface and versatile capabilities, Databricks enables users to build and deploy data engineering workflows, machine learning models, analytics dashboards, and more.integrating Databricks into an organization’s data ecosystem and implementing a robust data governance strategy can empower businesses to leverage their data assets effectively, make informed decisions, and stay ahead in today’s data-driven landscape.








